Book Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
Existing Skin Conditions
Acne
Schedule Your Dermal Filler Appointment with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Many existing skin conditions can make a person ineligible for Botox treatments.
Here are some examples:
-
Active Acne:
-
Rosacea:
-
Eczema:
-
Psoriasis:
-
Severe Skin Infections:
These conditions can make the skin more sensitive and prone to complications from Botox injections.
Botox can potentially worsen inflammation or infection in these areas.
It’s important to have healthy, clear skin before undergoing any cosmetic procedures, including Botox.
A doctor will assess your skin condition before recommending Botox treatment.
Acne, particularly severe acne, is a common reason people may be advised against Botox.
Here’s why:
-
Inflammation:
-
Botox injections can irritate inflamed skin and potentially worsen acne breakouts.
If you have active acne, it’s best to focus on treating it first before considering Botox.
Eczema
Numerous skin conditions can potentially interfere with or contraindicate the use of Botox.
Eczema, a common inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and often inflamed patches, is one such condition that requires careful consideration when considering Botox treatment.
The presence of active eczema lesions in the area where Botox injections are planned can increase the risk of complications such as infection, inflammation, or bruising.
Furthermore, the injection site may become more sensitive and irritated due to the existing skin barrier dysfunction associated with eczema.
It’s crucial for individuals with eczema to consult with a dermatologist or qualified healthcare professional before undergoing Botox treatment.
They can assess the severity of the eczema, its location relative to the intended injection site, and any potential interactions with other medications or treatments.
In some cases, it may be advisable to manage the eczema effectively through topical creams, moisturizers, or other therapies before proceeding with Botox injections.
Psoriasis
Various existing skin conditions can make individuals unsuitable candidates for Botox injections. One such condition is psoriasis.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to thick, scaly patches on the skin.
The areas affected by psoriasis often experience inflammation and sensitivity.
Injections into these regions can exacerbate symptoms, cause discomfort, and potentially spread the condition.
Botox injections may also interfere with the effectiveness of psoriasis treatments in some cases.
Before undergoing Botox treatment, it’s crucial to consult a dermatologist or medical professional.
They can assess your skin condition, determine its severity, and advise on whether Botox is appropriate for you.
Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Active Infections or Inflammations
Viral infections
Active infections or inflammations are a major contraindication for Botox treatment. Botox injections involve introducing a neurotoxin into the body, which can potentially worsen an existing infection or inflammation.
Viral infections, such as the common cold, influenza, or herpes simplex virus, are particularly concerning. The body’s immune system is already focused on fighting off the virus, and injecting Botox could divert resources and potentially complicate recovery.
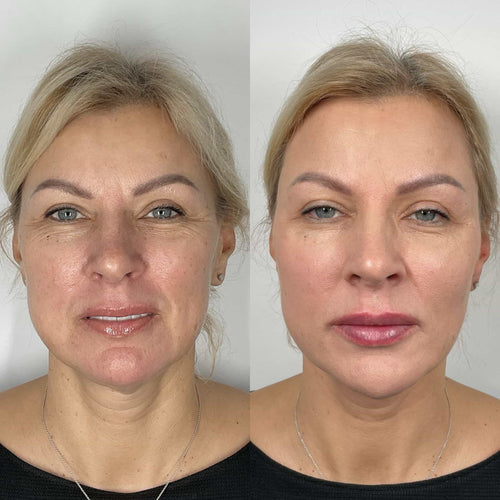
Inflammation at the injection site, such as from a skin infection or wound, also poses a risk. Injecting Botox into inflamed tissue can spread the inflammation or introduce bacteria.
It’s important for individuals with active infections or inflammations to wait until they are completely cleared before considering Botox treatment. This ensures optimal safety and minimizes the risk of complications.
Bacterial infections
Active infections or inflammations are a significant contraindication for Botox injections.
Botox works by temporarily paralyzing muscles, and injecting it into an area with active infection could worsen the condition. The risk of spreading the infection is also heightened, as the injection site becomes a potential entry point for bacteria.
**Bacterial infections**, such as cellulitis or impetigo, are particularly concerning. These infections can cause redness, swelling, pain, and warmth in the affected area. Injecting Botox into these areas could exacerbate inflammation and delay healing.
It’s crucial to ensure that any skin lesions or wounds are completely healed before considering Botox treatment.
The doctor will carefully assess your medical history and examine the injection site for signs of infection or inflammation before administering Botox. If an active infection is present, the procedure will be postponed until the infection has cleared up.
Inflammation near the injection site
Active infections or inflammations are a major contraindication for Botox treatment. Botox injections work by temporarily paralyzing muscles, and introducing it into an area with active inflammation could worsen the situation.
An active infection introduces bacteria or other pathogens into the body, triggering an immune response characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Introducing Botox into this environment could spread the infection further, potentially leading to complications.
Similarly, inflammation near the injection site signifies tissue damage or irritation. Injections could exacerbate these issues, delaying healing and increasing discomfort.
The presence of an active infection or inflammation at any point on the body can be a reason to postpone Botox treatment until the condition resolves completely.
Neurological Disorders
Alzheimer’s disease
Neurological disorders can present certain risks and complications when considering cosmetic procedures like Botox injections.
Here’s a breakdown of how neurological conditions may affect Botox treatment:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Individuals with Alzheimer’s disease may experience cognitive decline, making it difficult to understand the procedure, provide informed consent, or remember post-treatment instructions. Additionally, their weakened immune system could increase the risk of complications.
- Parkinson’s Disease: Botox can sometimes exacerbate symptoms like tremors and muscle rigidity in people with Parkinson’s disease. It’s crucial to consult a neurologist experienced in treating both conditions to assess potential risks and benefits.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS affects the central nervous system, leading to varying degrees of motor and sensory dysfunction. Botox injections can potentially worsen muscle weakness or trigger relapses in some individuals with MS.
- Stroke Survivors: Depending on the location and severity of the stroke, patients may experience muscle weakness, paralysis, or difficulty with coordination. Injecting Botox into affected areas could lead to unintended consequences or exacerbate existing neurological deficits.
Beyond these specific conditions, other neurological disorders that may affect Botox treatment include:
* **Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)**
* **Epilepsy**
* **Huntington’s Disease**
* **Neuropathy**
It’s essential to consult a qualified medical professional, preferably a neurologist or dermatologist with experience in treating neurological patients. They can thoroughly evaluate your individual medical history and determine if Botox is safe and appropriate for you.
Parkinson’s disease
Neurological disorders are conditions that affect the nervous system, which is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. These disorders can range in severity from mild to life-threatening and may cause a variety of symptoms, such as muscle weakness, paralysis, seizures, cognitive impairment, and sensory disturbances.
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement. It is caused by the progressive loss of dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the brain that controls motor function.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease typically develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include tremor, rigidity (stiffness), bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability.
While Botox is used to treat a range of medical conditions, there are certain neurological disorders that can prevent individuals from receiving it safely. The exact reasons depend on the specific disorder and its impact on the nervous system.
Individuals with neurological disorders should always consult with their healthcare provider before considering any treatment, including Botox. A thorough medical evaluation will help determine if Botox is a suitable option and identify any potential risks or contraindications.
Multiple sclerosis
Botox, a neurotoxin derived from bacteria, works by temporarily paralyzing muscles. This makes it an effective treatment for various medical conditions, including wrinkles, migraines, and muscle spasms. However, certain neurological disorders can make Botox administration risky or ineffective.
Here are some medical conditions that might prevent you from receiving Botox injections:
- ***Multiple Sclerosis***: MS is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, damaging the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibers. This damage can disrupt nerve signals and lead to a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, fatigue, and coordination problems. Botox injections could potentially worsen these symptoms or interfere with existing treatments.
- ***Parkinson’s Disease***: Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement. It causes tremors, stiffness, slowness, and difficulty with balance. While Botox can sometimes be used to manage certain muscle spasms associated with Parkinson’s, it can also have unintended effects on motor control.
- ***Myasthenia Gravis***: Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the communication between nerves and muscles. It causes muscle weakness and fatigue, particularly in the face, eyes, and throat. Botox injections could worsen muscle weakness in individuals with myasthenia gravis.
- ***Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome***: This is a rare autoimmune disease that affects nerve endings, leading to muscle weakness and fatigue. Similar to myasthenia gravis, Botox injections could potentially exacerbate symptoms.
It’s important to note that these are just some examples, and individual cases can vary. If you have a neurological disorder and are considering Botox injections, it is crucial to consult with your doctor to discuss the potential risks and benefits. Your doctor can assess your specific medical history and condition to determine if Botox is a safe and appropriate treatment option for you.
Back to Work Experts Detailed Weddings LA Pretty Little Answers James Martin Live On the Carpet
- Why Does My Lip Filler Look Bigger Some Days - November 6, 2025
- What Is The Difference Between CBD Gummy Sweets And Other Edibles - November 4, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Gummy Sweets For Energy - November 1, 2025

